Apparatus
Synthetic Chemistry Glass Apparatus used for wide range of expirements like Moisture Determination, Cyanide Distillation, Nitrogen Determination and many other applications
Introduction to Apparatus
In the scientific world, the term apparatus refers to carefully designed instruments and setups that enable experiments, research, and analysis. From the simplest glass beaker to advanced distillation units, every apparatus has a unique role in helping researchers achieve accuracy, reliability, and repeatability.
Among specialized laboratory apparatus, some of the most essential include the Dean Stark apparatus, simple distillation units, TKN and Kjeldahl distillation systems, Soxhlet complete assembly, Sulfite distillation setups, and Clevenger oil extraction units. These tools are widely used in chemistry, food science, pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, and industrial laboratories.
This comprehensive guide explores each apparatus in detail-covering its principle, construction, and applications, along with comparisons, safety practices, and future innovations.
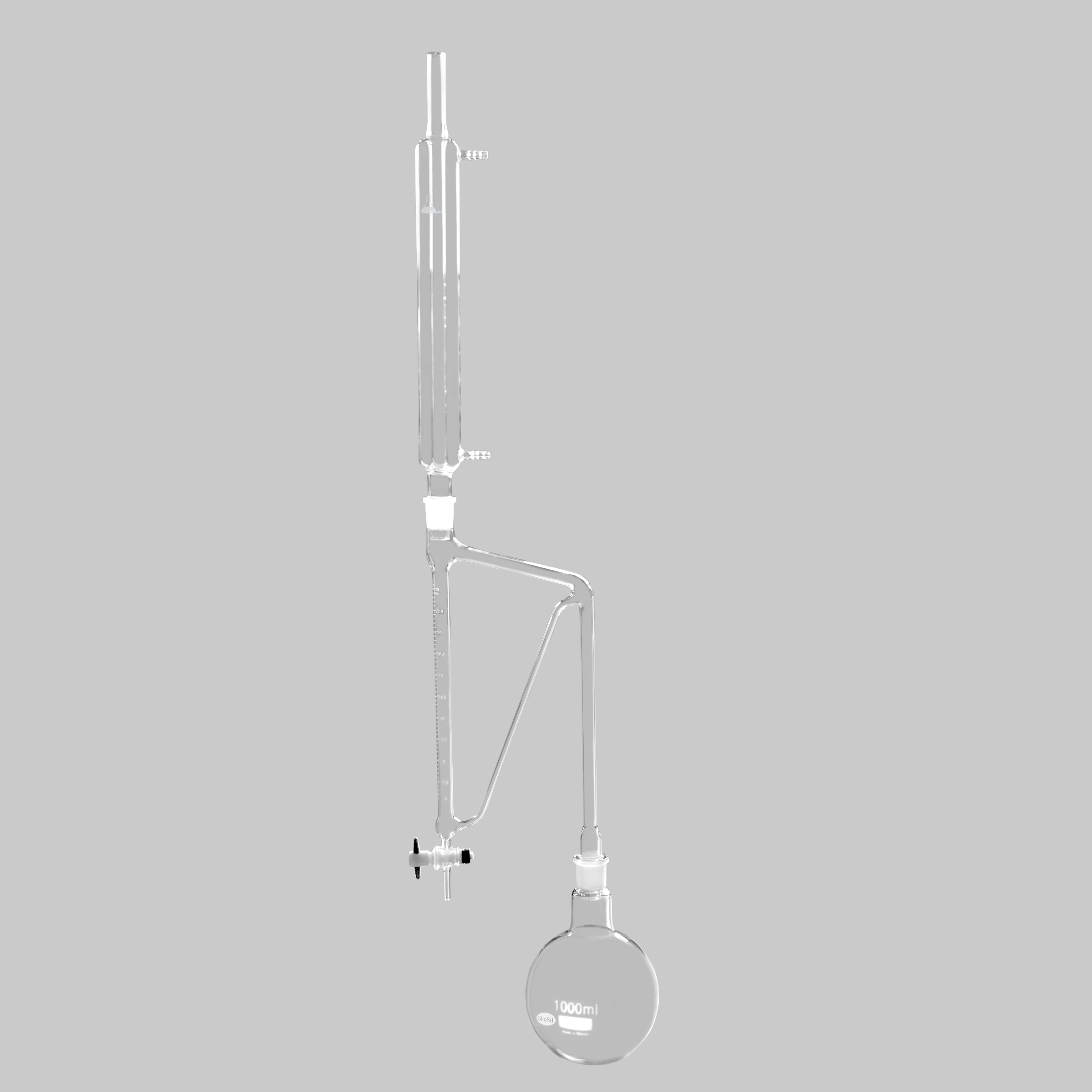
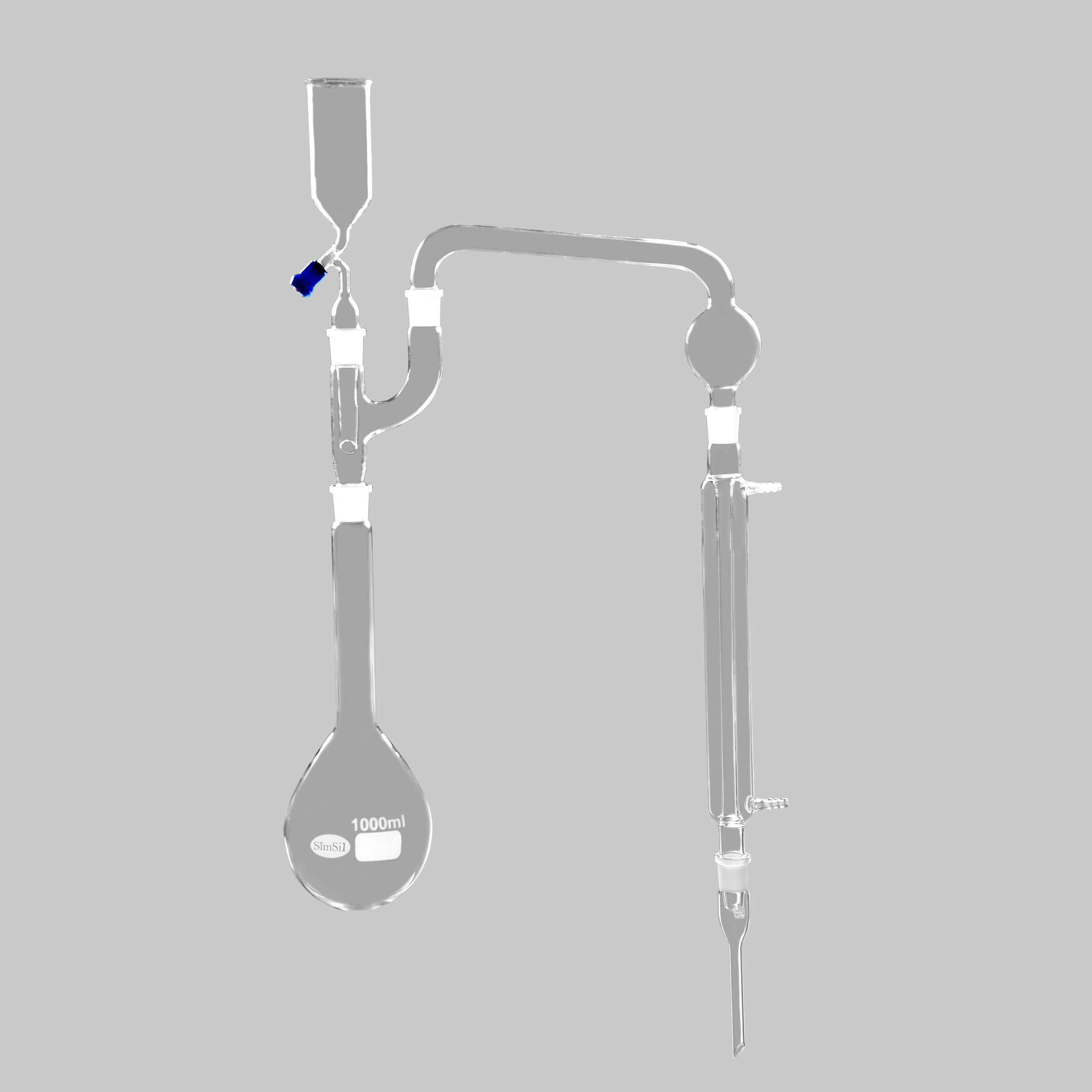
Dean Stark Apparatus
Principle of Operation
The Dean Stark apparatus operates on the principle of azeotropic distillation. It separates water from organic solvents by trapping it in a receiver, while the solvent cycles back to the flask.
Construction
-
Round-bottom flask: for reaction mixture
-
Condenser: cools vapors into liquid
-
Receiver tube: calibrated to collect water
Applications
-
Measuring water in petroleum products and lubricants
-
Moisture analysis in organic synthesis
-
Studying reaction mechanisms sensitive to water
-
Widely used in polymer and resin industries
Simple Distillation Unit
Working Principle
This apparatus separates liquids based on boiling point differences. The more volatile liquid vaporizes, condenses, and is collected separately.
Components
-
Distillation flask
-
Condenser
-
Receiving flask
-
Heat source (Bunsen burner or mantle)
Applications
-
Purification of solvents like ethanol and acetone
-
Preparation of distilled water
-
Educational use in teaching separation techniques
Note: For liquids with close boiling points, fractional distillation is preferred over simple distillation apparatus.
TKN Distillation Unit (Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen)
Principle
The TKN apparatus estimates nitrogen by converting organic nitrogen into ammonium sulfate through digestion. Ammonia is distilled, trapped in an acid receiver, and measured by titration.
Components
-
Digestion unit
-
Distillation chamber
-
Condenser
-
Receiver flask with boric acid
Applications
-
Determining protein content in food
-
Soil and fertilizer nitrogen analysis
-
Wastewater testing in environmental labs
-
Quality control in animal feed and beverages
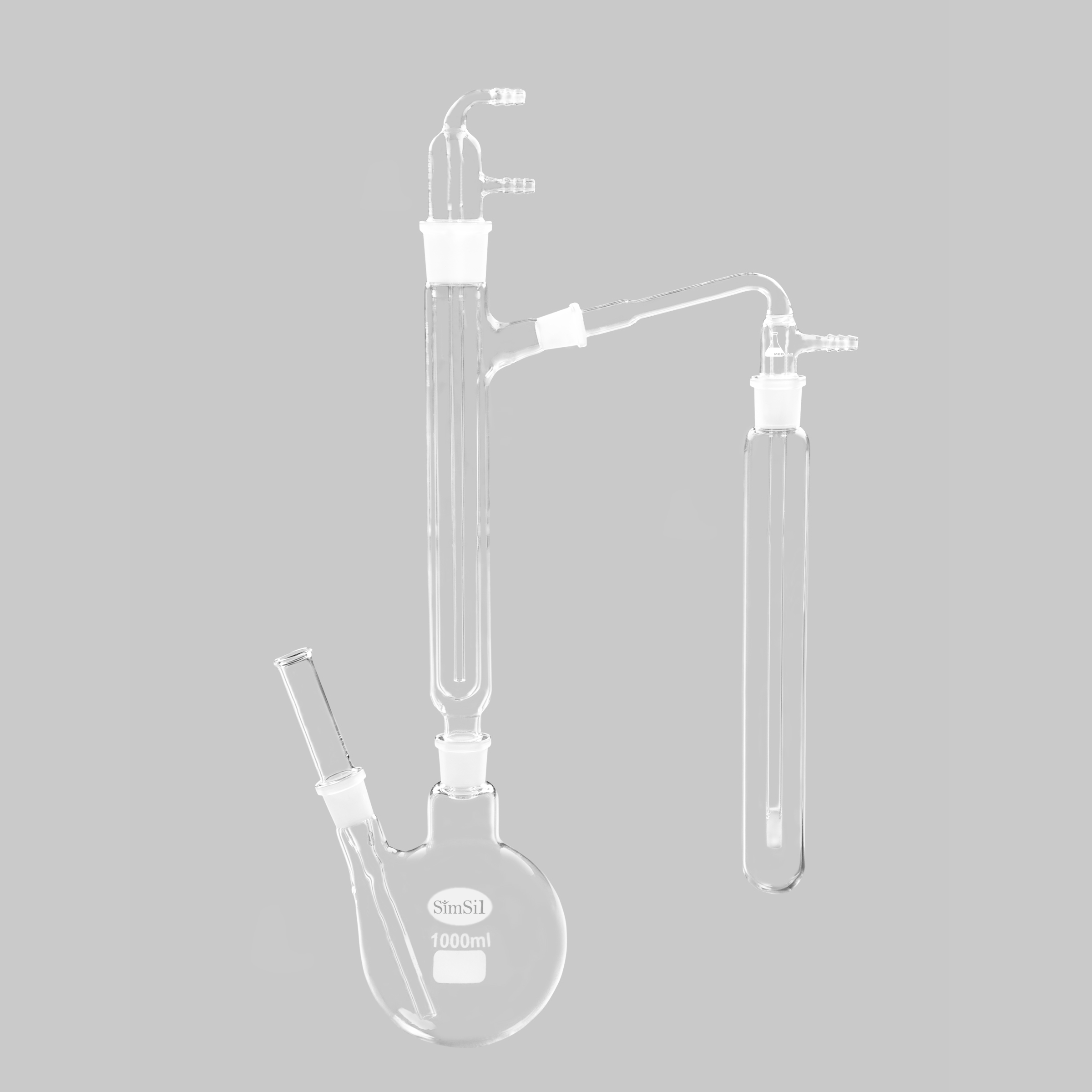
Soxhlet Complete Assembly
Principle
The Soxhlet apparatus uses continuous solvent extraction, where the solvent evaporates, condenses, and repeatedly washes the sample for efficient extraction.
Setup
-
Extraction chamber (holds sample)
-
Condenser
-
Siphon tube
-
Boiling flask (with solvent)
Applications
-
Extracting lipids from food samples
-
Isolating bioactive compounds from plants
-
Oil content determination in seeds and nuts
-
Research in pharmaceuticals and herbal chemistry
Sulfite Distillation Apparatus
Principle
This apparatus determines sulfur dioxide (SO₂) levels in samples. Distillation releases SO₂, which is absorbed in a receiver solution and quantified.
Applications
-
Ensuring safe sulfite levels in wines and beers
-
Food preservation analysis
-
Environmental monitoring of industrial emissions
-
Regulatory compliance testing
Kjeldahl Distillation Apparatus
Principle
The Kjeldahl apparatus measures nitrogen using digestion, distillation, and titration. It is the foundation for protein estimation methods.
Setup
-
Digestion flask with heating system
-
Distillation unit with steam generator
-
Condenser for ammonia capture
-
Receiver flask with standard acid
Applications
-
Protein estimation in food and beverages
-
Fertilizer nitrogen analysis
-
Pharmaceutical testing
-
Environmental monitoring
Difference between TKN and Kjeldahl apparatus: TKN measures organic nitrogen and ammonia, while Kjeldahl covers a broader range of nitrogen compounds.
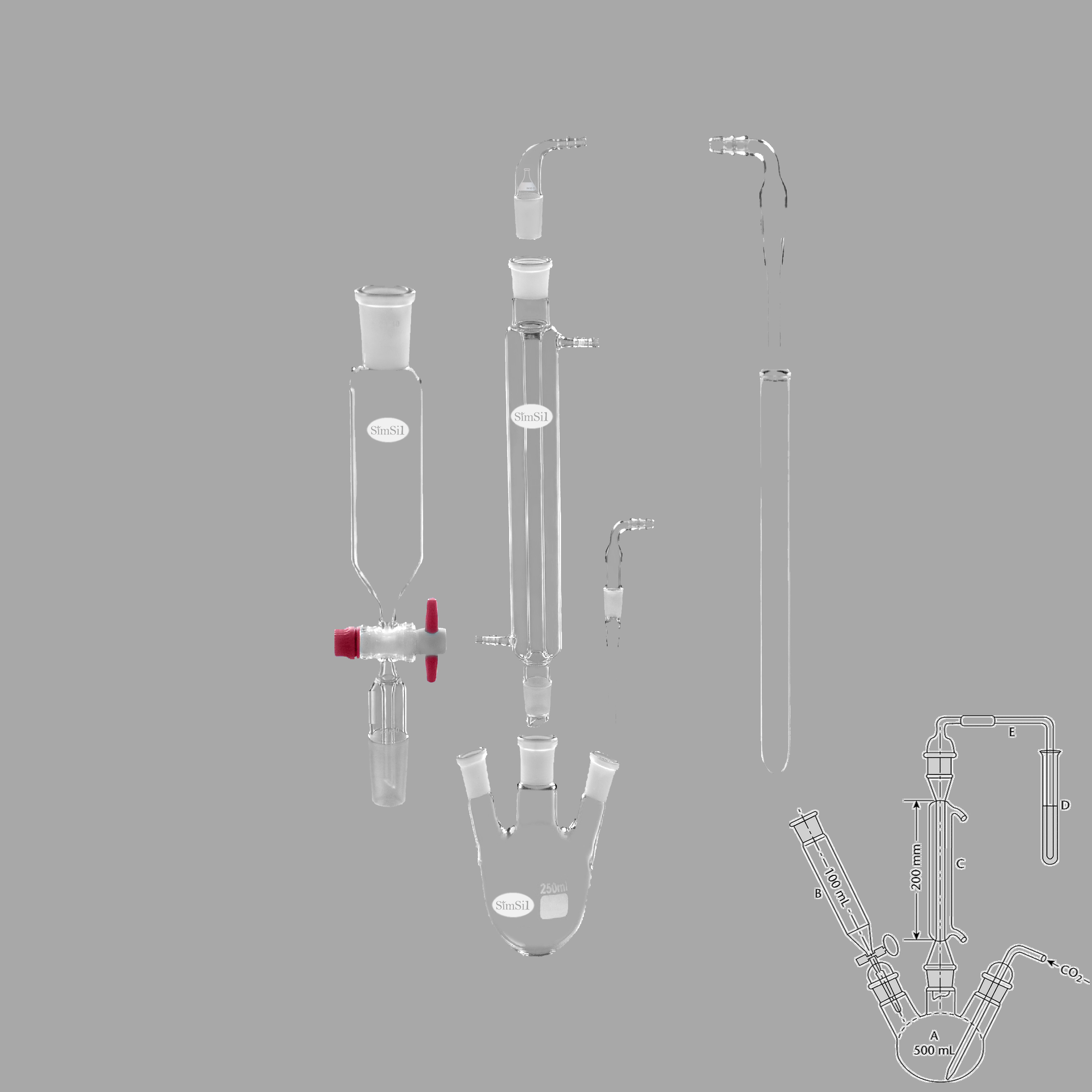
Clevenger Apparatus (Oil Heavier than Water – Complete Assembly)
Principle
The Clevenger apparatus is a type of steam distillation unit designed to extract essential oils from plant materials. For oils heavier than water, it ensures proper separation without mixing.
Construction
-
Boiling flask with plant material and water
-
Condenser for cooling vapors
-
Calibrated receiver tube to separate oil and water
Applications
-
Extraction of essential oils (e.g., clove, cinnamon)
-
Analysis of volatile aromatic compounds
-
Research in cosmetics, perfumery, and herbal medicine
Comparison of Specialized Apparatus
|
Apparatus |
Principle |
Main Use |
Industry Application |
|
Dean Stark |
Azeotropic distillation |
Water determination |
Petroleum, polymers |
|
Simple Distillation |
Boiling point difference |
Solvent purification |
Education, general labs |
|
TKN Unit |
Kjeldahl method |
Nitrogen measurement |
Food, agriculture |
|
Soxhlet Assembly |
Continuous extraction |
Oil & fat analysis |
Food, pharma |
|
Sulfite Distillation |
SO₂ release & absorption |
Sulfite analysis |
Wine, beverages |
|
Kjeldahl Distillation |
Nitrogen estimation |
Protein analysis |
Food, pharma |
|
Clevenger Assembly |
Steam distillation |
Essential oil extraction |
Cosmetics, herbal |
Safety Guidelines for Apparatus Operation
-
Always wear safety goggles, gloves, and lab coats
-
Handle volatile solvents inside a fume hood
-
Avoid overheating to prevent glass breakage
-
Regularly clean and calibrate apparatus
-
Store glass components carefully to prevent damage
Innovations in Apparatus Design
-
Automated Soxhlet and Kjeldahl systems reduce manual handling
-
AI-powered distillation units improve precision and data collection
-
Eco-friendly designs reduce solvent use and energy consumption
-
Integration with IoT sensors for real-time monitoring
Conclusion
Laboratory apparatus such as the Dean Stark, simple distillation unit, Soxhlet extractor, TKN and Kjeldahl distillation systems, Sulfite distillation setups, and Clevenger assemblies play a crucial role in modern science. Each apparatus has a specific purpose, from water determination and nitrogen estimation to oil extraction and sulfite analysis.
With advancements in automation, AI, and green technology, these apparatus are evolving to become safer, more efficient, and eco-friendly. For researchers, students, and professionals, mastering the use of these apparatus is fundamental to achieving accuracy in scientific research and industrial applications.
FAQs on Apparatus
Q1. What is the difference between Dean Stark and Clevenger apparatus?
Dean Stark measures water content in organic reactions, while Clevenger extracts essential oils.
Q2. Why is Soxhlet apparatus widely used in food labs?
Because it provides accurate measurement of fat and oil content.
Q3. Can TKN apparatus be used in pharmaceutical testing?
Yes, it is used for nitrogen analysis in drug formulations.
Q4. What makes Kjeldahl apparatus reliable?
It provides accurate protein estimation across multiple industries.
Q5. Is simple distillation suitable for crude oil separation?
No, crude oil requires fractional distillation, not simple distillation.
Q6. Why is sulfite distillation important in winemaking?
It ensures sulfite levels remain within safe regulatory limits.
Q7. Can Clevenger apparatus extract all essential oils?
Yes, but it works best for oils heavier than water.
Q8. Which apparatus is best for moisture analysis?
The Dean Stark apparatus is the gold standard.
Q9. Are automated apparatus better than manual ones?
Yes, automation improves safety, precision, and efficiency.
Q10. What precautions should be taken with distillation units?
Proper ventilation, heat control, and use of protective gear are mandatory.