Adapters
Laboratory Adapters are essential connectors used in scientific glassware setups to join, modify, or control the flow between different apparatus. Common types include straight adapters for direct connections, angular (bent) adapters to change the direction of flow, and vacuum adapters with sidearms for vacuum applications. Thermometer adapters securely hold thermometers in place, while Claisen adapters provide dual openings for additional attachments. Reducing adapters connect joints of varying sizes, and multiple neck adapters allow connections to several pieces of equipment at once. Cold trap adapters are used in vacuum systems to condense vapors, and adapters with stopcock offer precise control over fluid flow.
Introduction to Laboratory Adapters
Laboratories worldwide depend on precision tools to carry out experiments, research, and product development. Among these tools, laboratory adapters play a crucial yet often overlooked role. These small but powerful connectors bridge gaps between different types of lab glassware and instruments, ensuring that scientists can work efficiently, safely, and with great accuracy.
In this guide, we’ll dive deep into what laboratory adapters are, the different types available, their applications, benefits, and how to select the right one for your laboratory needs. Whether you’re a student, a researcher, or a professional chemist, this comprehensive resource will help you understand why adapters are indispensable in any lab setup.
What Are Laboratory Adapters?
Laboratory adapters are connecting pieces used to join glassware or instruments in a laboratory setting. They come in different shapes, sizes, and materials, making them versatile tools that enable scientists to build complex experimental setups. For instance, they can connect a condenser to a flask during distillation, attach tubing for vacuum filtration, or allow gas flow regulation.
Without adapters, laboratories would face significant challenges in creating leak-proof, stable, and safe experimental systems. They ensure compatibility across equipment and reduce the need for custom-made glassware.
Importance of Adapters in Laboratory Equipment
The significance of laboratory adapters lies in their ability to:
-
Ensure compatibility between different joint sizes and types.
-
Provide flexibility in experimental design.
-
Improve safety by preventing leaks and breakages.
-
Enhance cost-effectiveness by minimizing the need for custom glassware.
Adapters may look simple, but they are the backbone of many laboratory setups.
Types of Laboratory Adapters
Glass Adapters
Glass is the most common material for adapters because it is transparent, chemically resistant, and heat-stable.
Standard Taper Adapters
These adapters connect glassware with different joint sizes. For example, they allow a flask with a 24/40 joint to fit with a condenser of a different size.
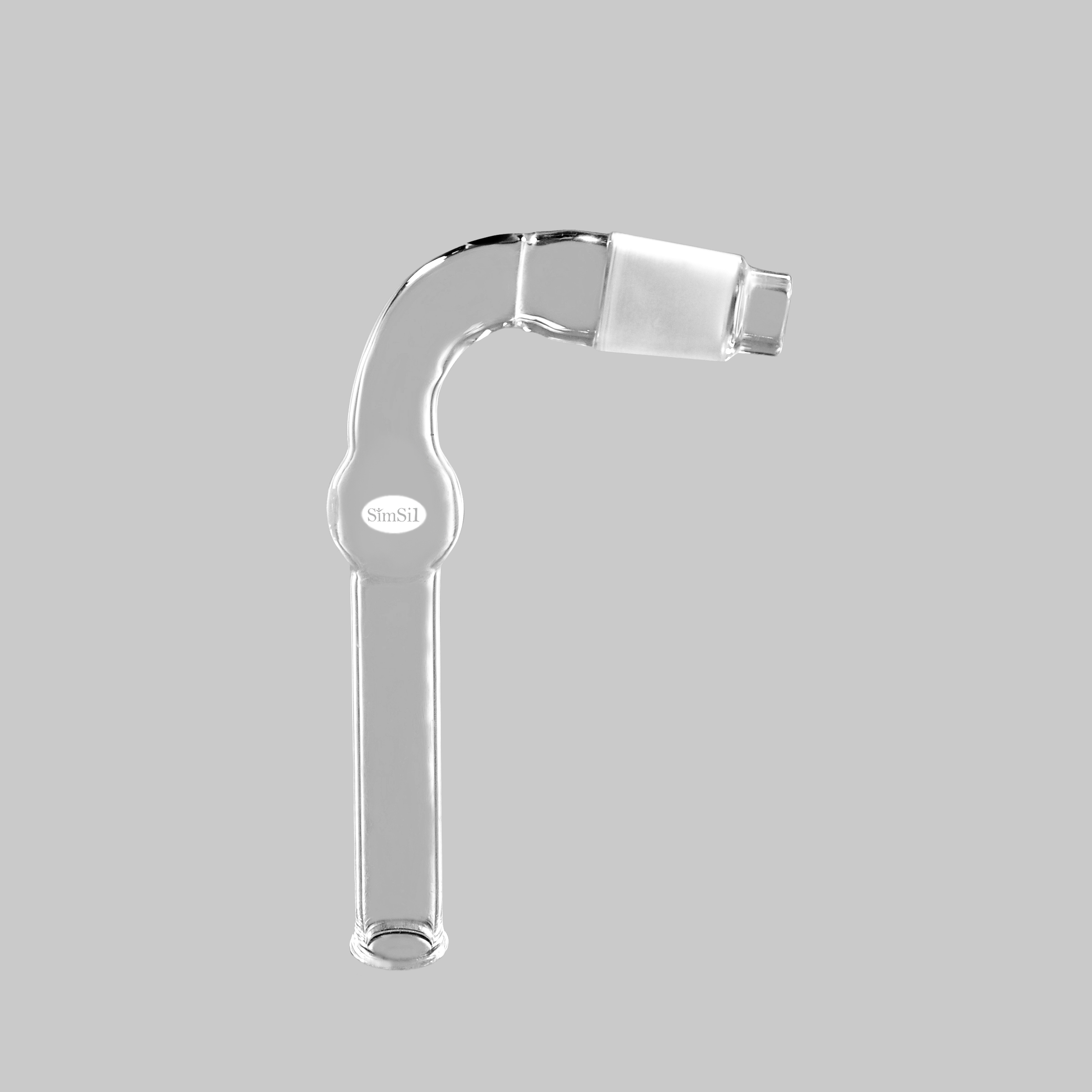
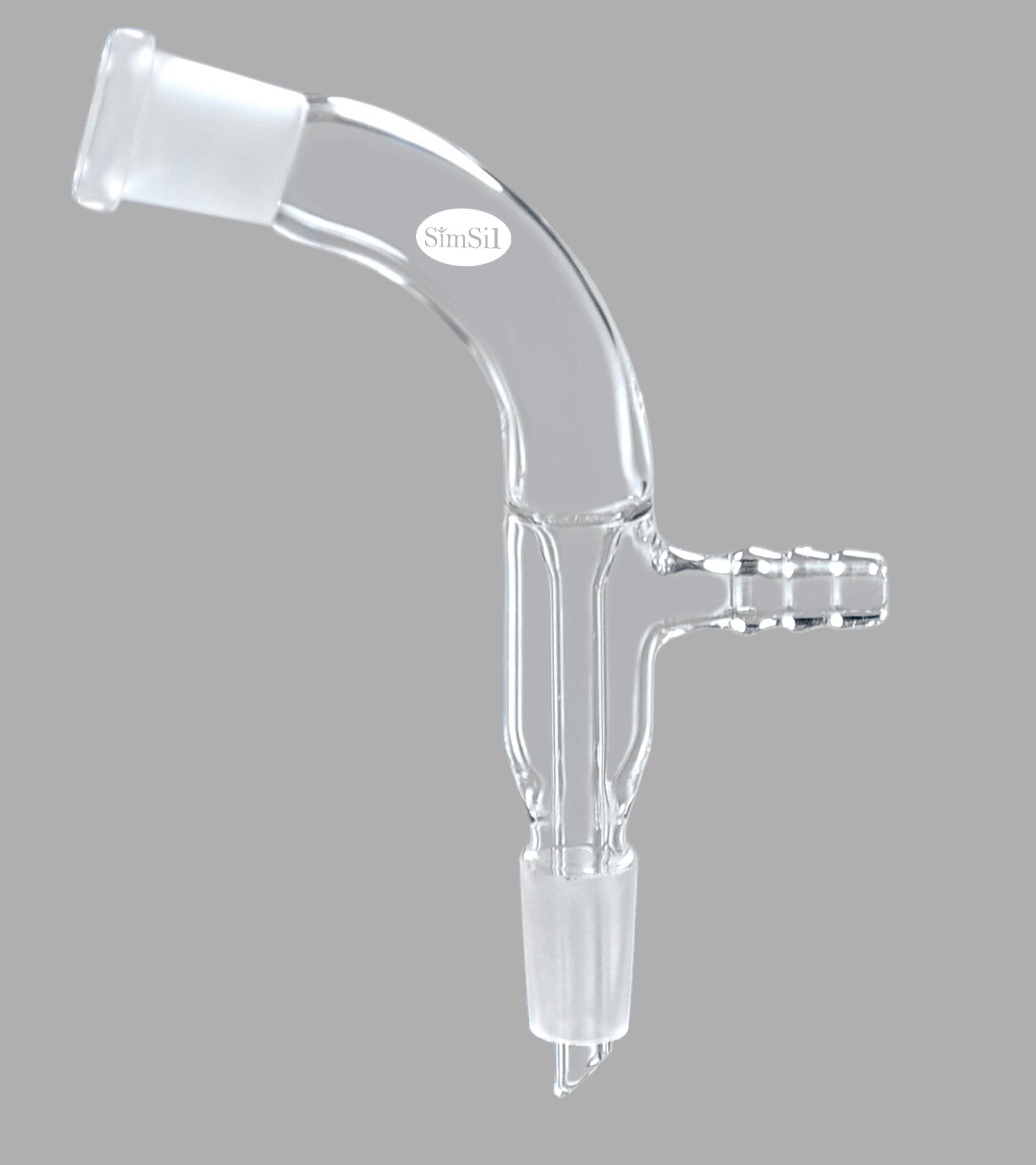
Vacuum Adapters
Designed with side arms for connecting tubing, vacuum adapters enable experiments involving pressure or filtration.
Claisen Adapters
A Claisen adapter is a Y-shaped connector that allows two different apparatus to connect to one joint, commonly used in distillation setups.
Plastic Adapters
Made from materials such as polypropylene or PTFE, plastic adapters are lightweight, resistant to breakage, and cost-effective. They are often used for educational purposes or low-temperature experiments.
Metal Adapters
Metal adapters, often made from stainless steel, are durable and suitable for high-pressure applications. They’re more common in industrial labs than academic ones.
Common Applications of Laboratory Adapters
-
Connecting glassware and instruments – Adapters allow for the seamless joining of lab equipment with mismatched joints.
-
Vacuum filtration and distillation – Specialized adapters help maintain airtight seals during processes requiring low pressure.
-
Gas flow and pressure regulation – Adapters with side arms or valves make it possible to introduce or remove gases safely.