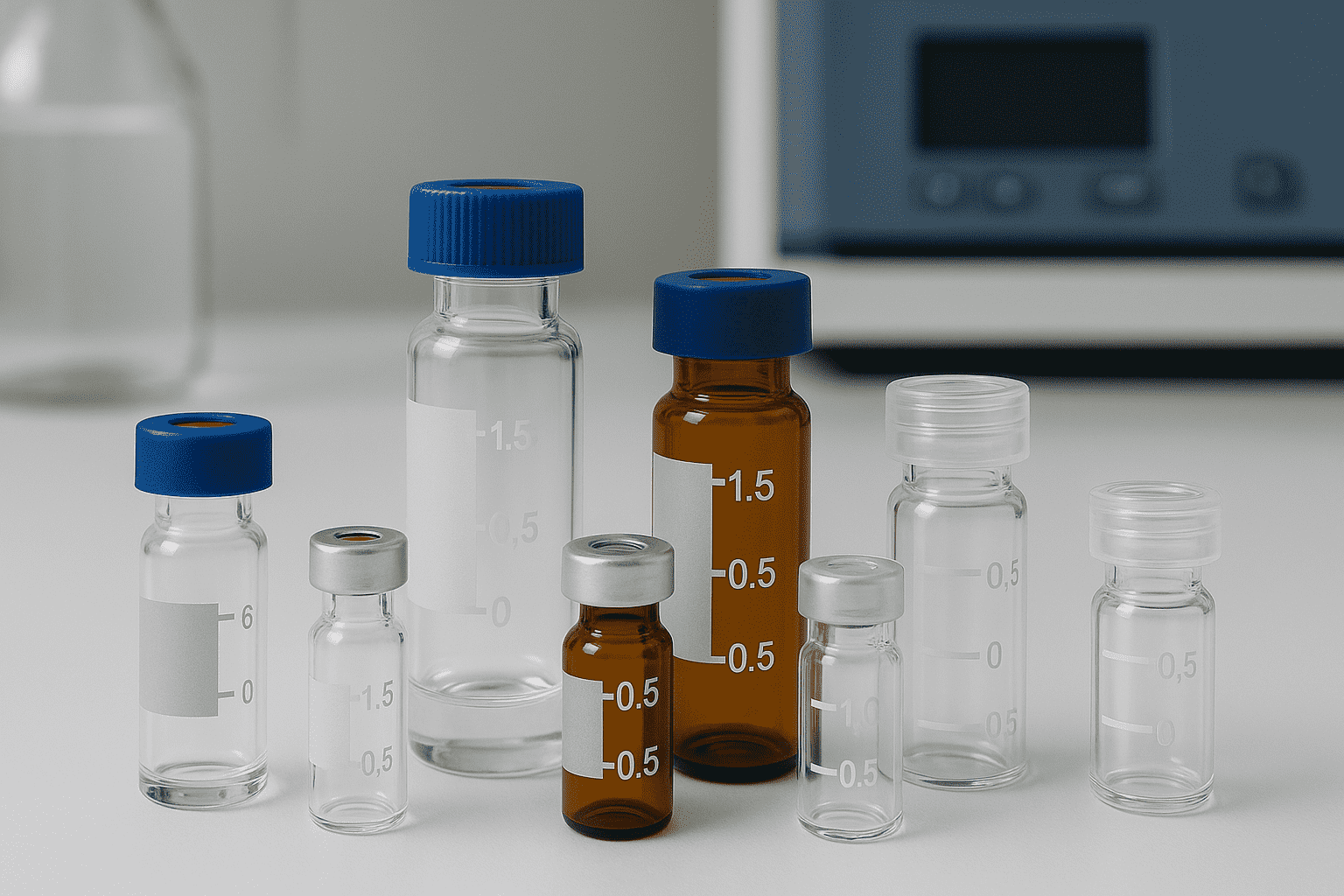Vials play an essential role in the modern world, quietly supporting industries from pharmaceuticals and laboratories to cosmetics and food technology. These small yet mighty containers preserve purity, ensure sterility, and maintain precision in storage and transport. In this ultimate guide, we’ll explore the different types of vials, their materials, manufacturing methods, and future trends shaping the packaging industry.
What Are Vials and Why Are They Important?
A vial is a small cylindrical container, typically made from glass or plastic, used to store liquids, powders, or samples. They’re designed to provide a secure, sterile environment that prevents contamination or degradation. Historically, vials date back to ancient times when apothecaries used glass bottles for medicine storage. Over the years, advances in material science and manufacturing technology have made vials more versatile and safer than ever.
The Evolution of Vials Through Time
The earliest vials were hand-blown glass bottles. With the industrial revolution, mass production enabled consistent sizes and quality. Today, automation and robotics ensure precise, contamination-free production. The introduction of polymer-based plastics has made vials lightweight, shatter-resistant, and eco-friendly.
Different Types of Vials Explained
There’s no “one-size-fits-all” vial. Different industries rely on specific designs depending on their use case.
Glass Vials
Glass vials remain the industry gold standard for pharmaceuticals. Borosilicate glass is prized for its heat resistance and chemical stability, while amber glass protects light-sensitive formulations. Soda-lime glass offers a cost-effective option for non-sensitive samples.
Plastic Vials
Plastic vials made from PET, HDPE, or polypropylene are ideal for portability and durability. They resist impact, reduce shipping weight, and are perfect for cosmetics or diagnostic kits.
Serum Vials vs Screw Cap Vials
Serum vials use rubber stoppers and aluminum seals for sterile pharmaceutical storage, whereas screw cap vials provide resealable convenience for laboratory and cosmetic use.
Materials Used in Manufacturing Vials
The choice of material impacts performance, durability, and cost.
Glass Composition and Strength
Glass vials are valued for transparency and inertness, ensuring that the stored substance remains unchanged. They can withstand sterilization at high temperatures and resist most chemicals.
Plastic Innovations
Modern plastic vials are increasingly eco-friendly, featuring BPA-free and recyclable polymers. Some are made from bio-based materials, aligning with sustainability goals.
Manufacturing Process of Vials
Glass Vial Production
The process begins with molten glass shaped into tubes. These tubes are cut and heated to form vial necks and bases. After annealing to relieve stress, each vial undergoes optical inspection for imperfections.
Plastic Vial Production
Plastic vials are created through injection molding or extrusion. The molten plastic is injected into a mold, cooled, and then sterilized. Automation ensures uniform thickness and leak-proof integrity.
Applications of Vials Across Industries
Pharmaceutical Industry
Vials are indispensable for injectable medicines, vaccines, and diagnostic reagents. They maintain sterility, prevent contamination, and comply with regulatory standards such as GMP and ISO 9001.
Laboratory Research
Scientists use vials to store and transport chemical samples, biological specimens, and reagents safely.
Cosmetics and Fragrance Sector
Luxury brands favor vials for perfumes and essential oils due to their elegance and precise dispensing control.
Food and Beverage Uses
In the culinary sector, miniature vials are used for flavor extracts, concentrated samples, and specialty oils.
Safety, Sterility, and Compliance Standards
Vials undergo strict quality testing to meet FDA, EMA, and ISO safety guidelines. Sterilization through gamma radiation or autoclaving ensures they are free from microorganisms. Tamper-evident seals protect integrity throughout distribution.